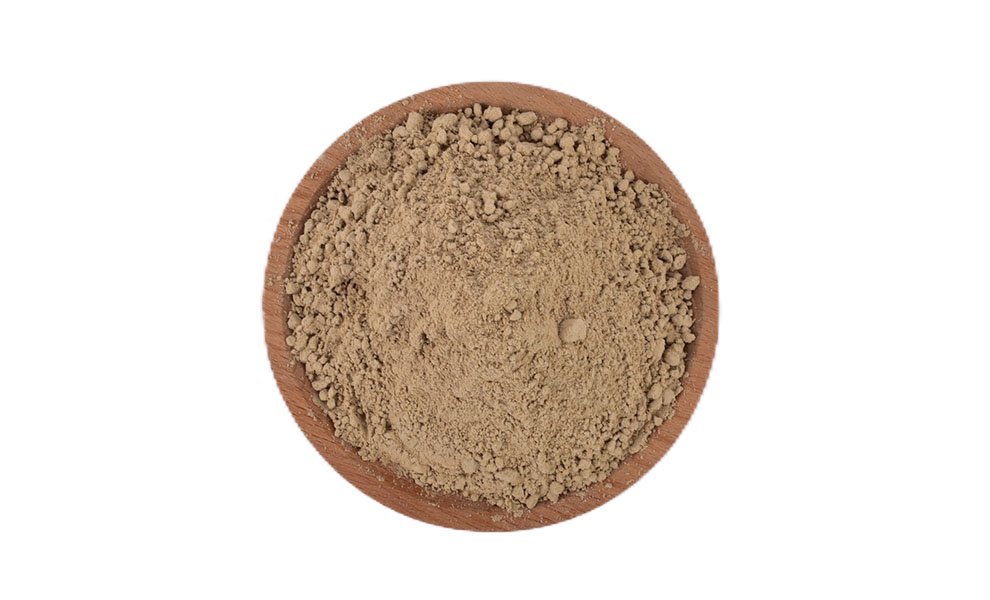
Rich in protein (73%), fat(4%), 18 kinds of amino acids, phosphorus, iron, potassium, sodium, vitamins and other trace elements necessary for animal growth. Rich in functional trace elements such as chitin, antimicrobial peptides, defensins, unsaturated fatty acids, etc. Has passed EU GMP+ and FDA certification.

 English
English Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Français
Français 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어